
Komodo DeFi Engine (KDE) previously known as Market Maker 2 (MM2) is the primary protocol that powers the atomic swap process. It allows Atomic DEX to be a market leader in the world of Decentralized exchanges. KDE is a complete suite of open-source blockchain development tools, which includes an atomic swap engine (backend/core), APIs and other set of programs and rules.
Before the Defi engine, the previous protocols used by AtomicDEX were not compatible and outdated to modern threats and user volume. There were two problems faced by the previous market makers.
Komodo uses the UTXO model as it is a Z-cash fork. There are a few blockchains in the world that use UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output model). These chains are usually Bitcoin or ZEC-related/forked blockchains. UTOX model is a very effective ledger management technique for a blockchain. They begin and end each transaction.
The internet is also not a seamless data connection all of the time. The previous market makers worked on open ports and specific firewalls. This was the second biggest problem faced by previous market makers. To work with a client-side p2p exchange, the internet connection is really important. This makes sure that the app is completely in sync with the blockchain so there won't be any hurdles while having an exchange.
KDE uses libtorrent which implements BitTorrent protocol. This helps KDE operate without any connectivity gaps and network anomalies. In this protocol, the swap works in a torrent type of way. This shows the level of dedication and creativity the atomic DEX team has towards this technology.
Here is a step by step breakdown on how Atomic DEX allows peer to peer atomic swaps from both a maker and taker perspective.
(Steps you’ll see when swapping coins)
If a Maker posts a trade on AtomicDEX it is registered as Step 0. This is not a part of the trading process but it is important as it is initiating the trade. This can be called STEP 0.
(Click on the Trade button to initiate a trade (STEP 0))
Step 1: <DEXfee> payment
The Taker which will usually see an order to fill trades on a Maker’s offer and accepts it. In order to verify the trade taker will pay a fee of 0.15% of the total trade amount. The purpose of the swap fee is to get rid of spam requests. Note that Makers do not pay any trading fees on AtomicDEX.
After the taker has paid the exchange fee the maker will verify and move on to step 2 which will be sending the maker payment. Please note all of this is possible due to Market Maker 2 and automated. You don’t have to literally verify it yourself.
Step 2: <MakerPayment> Is Sent
Maker sends his payment, known as the Maker Payment, which is sent to a P2SH address (for Bitcoin-protocol coins) or to a smart contract address (for ETH and ERC-20 tokens).This commits senders funds to a hash.
Step 3: <TakerPayment> Is Sent
Once the Maker payment is sent to a hash locked or time locked address the taker payment is sent using the same algorithm in a hash locked address which will be transferred later on to the wallet address.
Step 4: <TakerPayment> Is Spent
Once the taker payment is hash locked the maker payment is released from the time lock into the personal wallet address of the taker. This is possible once a secret 32 byte hash code is revealed.
Step 5: <MakerPayment> Is Spent
Similarly, the taker payment is unlocked in the same mechanism and sent to the maker's personal address. The secret byte code is public once the time lock is complete upon successful transaction.
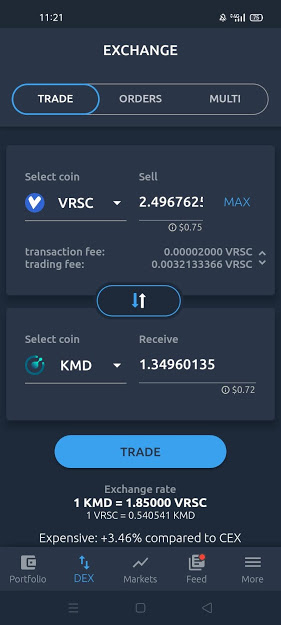
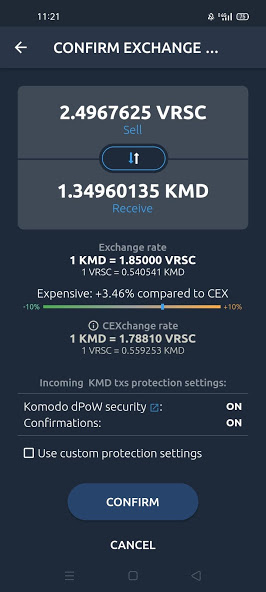
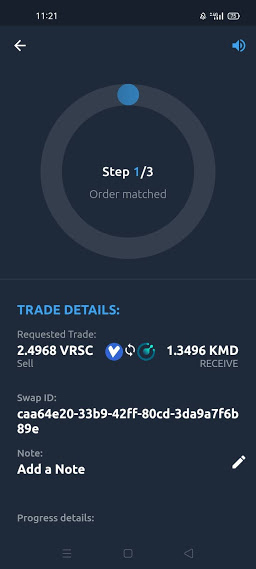
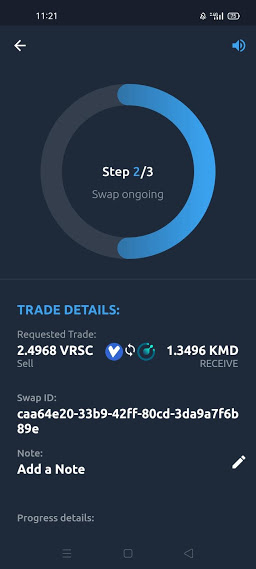
This long and technical process is automated and only possible due to the komodo defi engine. The engine runs automated and secure while keeping the network secure, seamless, and quick. Developers can refer to docs if they want to use the public APIs.
