
There are some prerequisites for you to better understand blocks. These prerequisites are terms you frequently come across when you hear about Blockchain and you will see them throughout this article.
Blockchain is a digital distributed ledger or database of transaction records that consist of immutable data in a chain form with each record set known as a BLOCK followed by another block. These blocks are immutable and any changes will follow up and change the entire blockchain set since they follow each other.
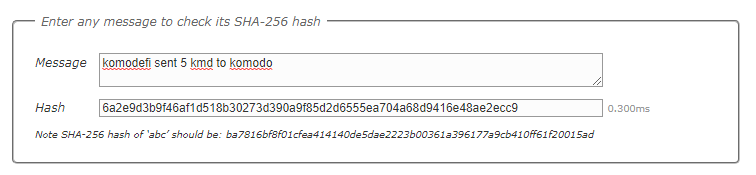
Hashing is a one-way cryptographic formula to check the validity of any input (Strings, chars, etc) and convert it into a hash-value which is irreversible and cannot be converted back to the original input.
In a blockchain, each block is encoded by a hash which is a fixed output problem that is being solved by multiple nodes (Computers), and upon correctly guessing the solution the network creates a new block and moves any pending transactions from the older block to the newer block.
The system rewards the node that made the correct guesses in form of a block reward. More specifically, the system creates a mathematical problem and you (node) need to guess the solution to generate a new block for the blockchain and earn the reward for the solution.
Of course, this is all done by your computer and the more powerful the machine the more guesses it will make per second (hash rate) increasing the chances of making a correct guess.
The mechanism that is used for a decentralized network or blockchain is to maintain trust. security and finality between nodes or distribution of the network is called a Network consensus or Blockchain consensus.
This mechanism is unique throughout the blockchain and all parties involved within the system agree upon this method to make any operation in the blockchain.
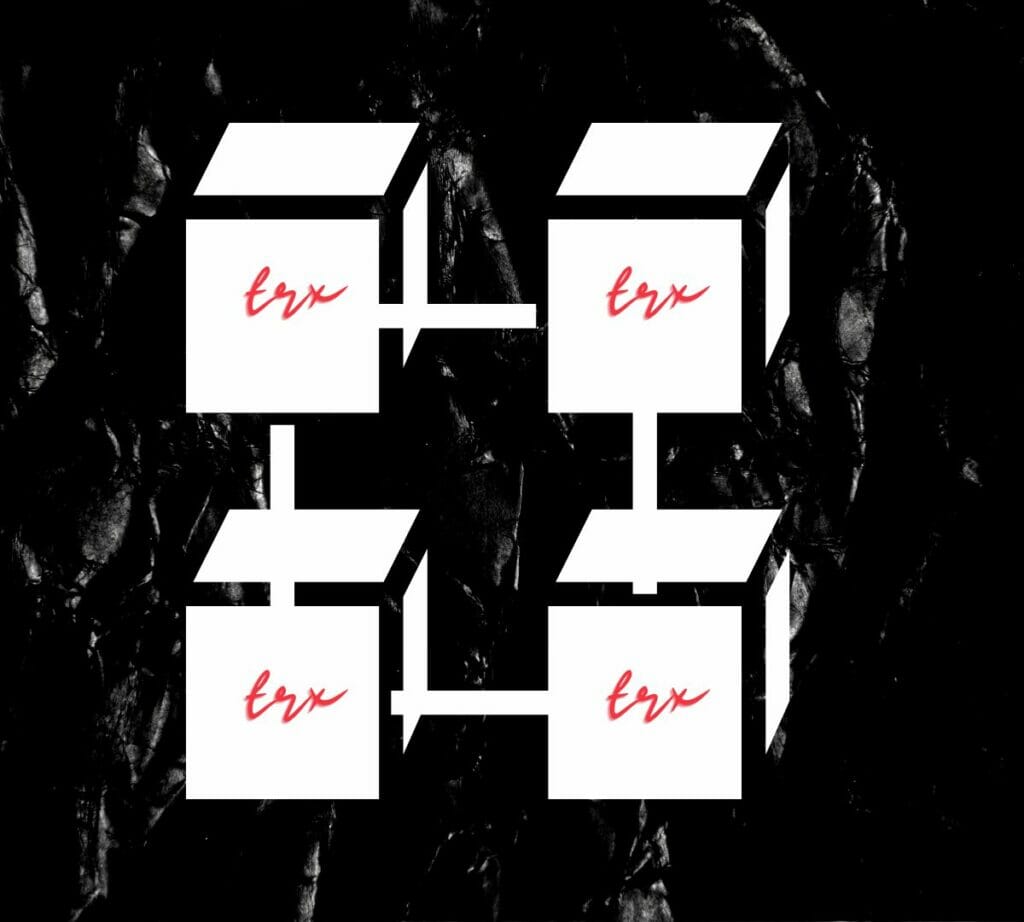
Block is a data structure in a blockchain database that usually store data, transaction hash, and the hash of the previous blocks to create a chain of blocks. In some special blockchains, it can also store special data types, i.e supply chain blockchains or gaming blockchains.
Blocks work as homogenous data structures depending on the type of blockchain protocol. I.E, Bitcoin block stores the data of sender, receiver, and amount with a transaction hash of the current and previous block.
These blocks are immutable to ensure safety and any kind of changes made in these blocks will affect the entire blockchain, this is possible due to the correlation between blocks. The block hash algorithm is almost impossible to guess and take over the network.
Just like building blocks, they are the foundation and the very thing that make up a blockchain. There is always a limit to the storage capacity of a block which demands newer blocks for a network to reduce congestion and ensure that there is an incentive and interest for nodes involved with the blockchain.
Generating newer Blocks also means multiple parties are invited to the network so which ensures the network is really distributed and decentralized as multiple nodes are being connected to the network removing any single central authority.
You might have often heard about making money by mining or minting, to simplify, this is the part where people are getting paid, basically for creating new blocks.
Different protocols have different network consensus which results in different techniques to create a new block. There are two main consensus mechanisms as of today with many modified but subordinate versions:
In this model, blocks are generated by working for the network and solving the hashes using heavy machines or mining equipment (ASIC machines). The block is distributed and everyone can get involved and try to solve the hash.
A proof of work model encourages miners to compete with each other to guess the correct block hash first. A lot of computation power and energy is needed to mine coins and generate new blocks to make sure a POW blockchain is online and secure.
Proof of stake consensus is contrary, less-hectic and a bit unfair type of network consensus. In a proof of stake consensus, the validators (miners in POW) are chosen at random and only one out of many validators are chosen to create a new block and get rewarded.
These validators stake huge amounts of coins which are locked away as long as they are validating the network, this creates a monopoly for validators with bigger shares in the network.
This system is more eco-friendly and scalable in a way as it randomly chooses from a fixed number of validators to create a new block and mint rewards that are validated by all the validator nodes present in the systems. Geavy hardware and power consumption is redundant.
