
Traditional money exchange is a really simple and obvious concept when looking at the history of money. For instance, you visit Europe, you land at the airport and exchange your Dollars for Euros because Europe does not use Dollars in their domestic market. While in some or most countries you don't even need to bother exchanging paper money. This seems really easy in traditional finance because of the universal acceptance of Paper Money.
The colossal acceptance and ease of exchanging paper money are expedient because of a central authority and world bank. These institutions accept and administer almost all of paper currency/FIAT currency in the world. Paper money has been almost forever.
The on-hand problem with cryptocurrencies is the lack of interconnectivity between distinct protocols and networks. This restricts blockchains and cryptocurrencies to be a routine or casual system for the general public as opposed to paper money or traditional finance.
Blockchain bridges can result in scaling the cryptocurrency world, which will allow the secure exchange of blockchains having different networks or protocols without the need for a third-party exchange, creating cashless economies and DAO (decentralized autonomous organization) a reality.
A cryptocurrency is a digital currency powered by a database or distributed ledger called a blockchain. Each blockchain is developed on a mechanism, set of rules, or protocols we call a consensus. This consensus defines the features and protocols of a network or blockchain and its interaction with transactions.
These cryptocurrencies have different networks to run their own smart contracts, tokens, or subsets. The most overblown networks today are Bitcoin and Ethereum. These two cryptocurrencies have an entirely different approach towards their networks.
Bitcoin does not have any smart contracts capabilities, there are no other cryptocurrencies/tokens running on the Bitcoin network/blockchain. The coins derived from the bitcoin codebase are not related to bitcoin but somewhat use bitcoin's p2p mechanism or other libp2p implementations.
Whereas Ethereum has a huge list of smart contracts and decentralized applications on its network. This is because of smart contract capabilities and constant development and extension into entirely different ecosystems such as Binance Smart Chain, Matic, Cardano, etc. Ethereum was the first blockchain to introduce smart contracts.
These two networks can not be connected together for the interchange of data hence we need a blockchain bridge to connect two or more networks together while being completely trustless.
The tokens built on Ethereum's network are called smart contracts. These contracts will have the same address as an Ethereum address starting with 0x. They can have different use cases and are classified into a predefined set of tokens such as ERC-20, ERC-721, etc.
These smart contracts can run on the Ethereum network. These smart contracts or tokens can be treated as a cryptocurrency such as USDC which is the crypto version of the US dollar. USDC is an ethereum token always equivalent to one US dollar. To send/receive USDC the network will charge Ether in fee for using its network.
Another Popular Network with smart contract capabilities is Polygon Network. Polygon network can also have pegged tokens or its own version of another cryptocurrency but to conduct any transaction it will use MATIC in transaction fee, making MATIC the primary cryptocurrency of the network.
Ethereum is the most complex network as of today. The introduction of smart contracts and network pegged tokens has increased the network traffic eventually reducing the speed and increasing the transaction fees for transactions. Here are a few reasons why bridges are needed while keeping Ethereum in context.
The dominance of the Ethereum network has somewhat forced most of the cryptocurrency brokers and exchanges to sell Ethereum versions of a cryptocurrency instead of the native version. These versions of another cryptocurrency are called pegged tokens. Every cryptocurrency has an ERC-20 version of it running on the Ethereum Network.
For example, if you buy Polygon from Coinbase, it does not provide you native polygon token but instead an ERC-20/smart contract version of Polygon having an Ethereum address, running on the Ethereum network.
The network traffic has made Ethereum a lot slower and a lot expensive compared to other networks. The biggest competitor of Ethereum is Solano which can perform more than 10x the transactions at less than 100x cheaper rates.
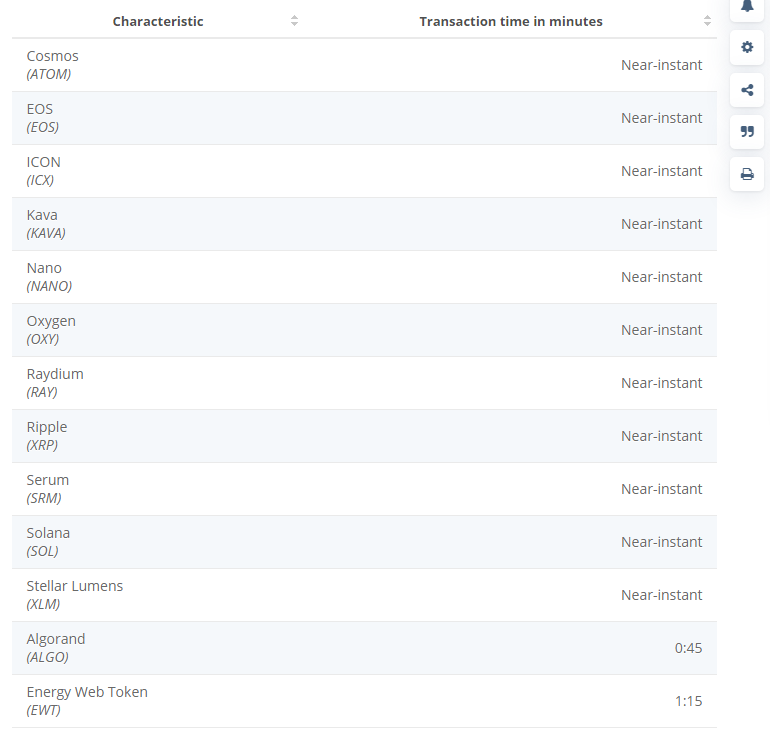
The transaction speeds of Ethereum are currently lower than 48 other cryptocurrencies or networks. This makes Ethereum a really slow network compare to Solano or Polygon.
The average transaction fee of Ethereum is $44 according to BitInfoCharts (Taking an Average of the last 2 years). The prices rose from less than a dollar to $52 as of January 2022 for the last 2 years. This makes Ethereum the most expensive network as of today despite a surge in the market value of Ethereum.
The biggest drawback of the Ethereum network is scalability issues. Bitcoin brought peer-to-peer transactions to the table while maintaining security, anonymity, and transparency. This made Bitcoin revolutionary as it served the basic purpose of a decentralized currency.
Cryptocurrencies are built to access for all, without any bounds or restrictions. Bridges will allow Ethereum to scale between networks, solve some security issues whilst introducing new security issues, and connect different blockchains together as a whole in averse to traditional finance, centralized economy.
There are 2 different designs of bridges. These classifications can be made on centralized and decentralized characteristics.
The easiest version of a network bridge is a liquidity pool. These liquidity pools are backed by institutions or private investors that lend different cryptocurrencies in order to earn fees. These cryptocurrencies are pooled together and spent/exchanged as ordered by a market maker.
A bit more complex but a decentralized method of network bridge is via smart contract. In this method, a pegged token of another cryptocurrency is developed on the network in exchange for the native coin.
This pegged token will have the same price as the native asset but will not have the same characteristics as the native asset. This smart contract method is mostly used for coins that don't have smart contract capabilities.
For example, renBTC is a token that allows you to hold an Ethereum version of Bitcoin with the same price. This version of Bitcoin can be used within the Ethereum network using an Ethereum address.
A blockchain bridge does not imply a specific method or protocol instead a practice or term for interconnectivity of distinct blockchain networks via different methods.
Blockchain bridges are a need of the moment and many cryptocurrencies are in the works to make functional bridges with secure means to scale their networks and improve onboarding. Verus is also working on a decentralized bridge to connect with the Ethereum network.
Bridges can make cryptocurrencies more popular and widely accepted if not better but near the colossal scale of FIAT acceptance around the globe.
